Co-ordinate Geometry Class 9
Co-ordinate Geometry Class 9
Distance between points (x1,y1) and (x2, y2)
=√ (x2 - x1)^2 + ( y2 - y1)^2
Exercise :
Q 1. Find the distance between following points :
i) (3 , 5); (6, 9 )
=√ (x2 - x1)^2 + ( y2 - y1)^2
=√ (6 - 3)^2 + ( 9 - 5 )^2
=√ 3^2 + 4^2
=√ 9 + 16
=√ 25
= 5
ii) (1, 2) and ( -5, -6)
=√ (x2 - x1)^2 + ( y2 - y1)^2
=√ (-5 -1)^2 + ( -6 -2)^2
=√ (-6)^2 + ( -8)^2
=√ 36 + 64
=√ 100
= 10
iii) (-2, -5) and ( 6 , -20)
=√ (x2 - x1)^2 + ( y2 - y1)^2
=√ (6 + 2 )^2 + ( -20 + 5 )^2
=√ (8)^2 + ( -15)^2
=√ 64 + 225
=√ 289
= 17
iv) (13/2, -15/4) and ( -5/2, 33/4)
=√ (x2 - x1)^2 + ( y2 - y1)^2
=√ (-5/2 -13/2)^2 + ( 33/4 + 15/4)^2
=√ (-18/2)^2 + ( 48/16)^2
=√ (-9)^2 + (12)^2
=√ 81 + 144
= √ 225
= 15
v) ( 3√3, 6) and ( √3, 4 )
=√ (x2 - x1)^2 + ( y2 - y1)^2
=√ (√3 - 3√3)^2 + ( 4 - 6)^2
=√ (-2√3)^2 + ( -2 )^2
=√ 12 + 4
=√ 16
= 4
Q 2.
i) A is on x-axis with abscissa 4 and B = ( -1, -12). Find the distance between A and B.
Solution.
Using distance formula
A is on x- axis and its abscissa is 4.
Co-ordinates of A are ( 4, 0) and B ( -1, -12)
Distance between A and B
= √ ( -1 - 4)^2 + ( -12 - 0 )^2
= √ (-5) ^ 2 + (-12)^2
=√ 25 + 144
= √ 169
= 13
ii) P lies on y- axis and its ordinate is 3.
Co - ordinates of P are ( 0 , 3) and Q ( 12 , - 13)
Distance between P and Q is
= √ ( 12 - 0)^2 + ( -3 - 13)^2
=√ 12^2 + 16^2
= √ 144 + 256
=√ 400
= 20
Q 3. Find the co-ordinates of circumcentre of △PQR where P = (6, -5), Q = ( 6, 7) , R = ( 8 , 7).
Solution :
Using distance formula,
P = (6, -5), Q = ( 6, 7) , R = ( 8 , 7)
O is the circumcentre of △PQR
OP = OQ = OR
Let co-ordinates of O be ( x, y)
OP^2 = ( x - 6 )^2 + (y + 5)^2
OQ^2 = ( x - 6 )^2 + (y - 7)^2
OR^2 = ( x - 8 )^2 + (y - 7)^2
since OP = OQ
OP^2 = OQ^2
( x - 6 )^2 + (y + 5)^2 = ( x - 6 )^2 + (y - 7)^2
y^2 + 10y + 25 = y^2 - 14y + 49
10y + 14y = 49 - 25
24y = 24
y = 24/24 = 1
Since OQ = OR
OQ^2 =OR^2
( x - 6 )^2 + (y - 7)^2 = ( x - 8 )^2 + (y - 7)^2
x^2 - 12x + 36 =x^2 -16x + 64
-12x +16x = 64 - 36
4x = 28
x = 7
Co-ordinates of circumcentre be Q (7,1)
Q 4. Find the co-ordinates of a point on x - axis which is equidistant from A (2, -4) and B(8,4).
Solution
Let the point on x-area be P(x,0)
and given points A and B are A (2, -4), B(8, 4)
Since PA = PB
PA^2 = PB^2
PA^2 = (x -2)^2 + (0 + 4)^2
and PB^2 = (x - 8 )^2 + (0 - 4)^2
(x -2)^2 + (0 + 4)^2 = (x - 8 )^2 + (0 - 4)^2
x^2 - 4x + 4 +16 = x^2 - 16x + 64 +16
-4x + 16x = 64 +16 - 4 -16
12x = 60
x = 60/12
x = 5
Required co-ordinates of P are (5,0).
Q 5. Find the co-ordinates of a point P on y-axis so that PA = PB where A = (-2, 4) and B = ( -5, -3 ).
Solution .
Let co-ordinates of point P on y - axis be ( 0, y)
and A ( -2, 4) , B (-5, -3) and PA = PB
PA^2 = (0 + 2)^2 + (y - 4)^2
PB^2 = (0 + 5)^2 + ( y + 3)^2
PA = PB
PA^2 = PB^2
(0 + 2)^2 + (y - 4)^2 = (0 + 5)^2 + ( y + 3)^2
4 + y^2 - 8y +16 = 25 + y^2 + 6y + 9
-8y -6y = 25 + 9 - 4 - 16
-14y = 14
y = 14/-14 = -1
Co-ordinates of P are (0,-1).
Q 6. P is point on x -axis and abscissa -6 and Q is (2,15). Find the distance between P and Q.
Solution .
P is point on x-axis and abscissa is -6 and Q be the given point ( 2, 15)
Co-ordinates of P are (-6,0)
Now, PQ^2 = (x2 - x1)^2 + (y2 - y1)^2
= ( 2 + 6)^2 + (15 + 0)^2
= (8)^2 + (15)^2
= 64 + 225
= 289
PQ = √ 289 = 17 units
Q 7. Find the co- ordinates of points whose abscissa is -4 and which are at a distance of 15 units from (5, -9)
Solution:
Let co-ordinates of P be (-4, y) and Q is (5, -9) and distance between them is 15 units
(5 + 4)^2 + (-9 -y )^2 = 15^2
9^2 + 81 + y^2 +18y = 15^2
81 + 81 + y^2 +18y = 15^2
162 + y^2 +18y = 225
y^2 +18y = 225 - 162
y^2 +18y = 63
y^2 +18y - 63 =0
y^2 + 21y - 3y -63 = 0
y(y + 21) -3(y + 21) = 0
(y + 21) (y - 3) = 0
either (y + 21) = 0 or (y - 3) = 0
y = -21 or y = 3
Co-ordinates of P will be (-4, -21) or (-4,3)
Q 8. Prove that A(-5,4), B(-1,-2) are the vertices of an isosceles right angled triangle.
Solution.
Given Points are A (-5, 4), B(-1, -2), C( 5, 2)
AB^2 = (-1 + 5)^2 + ( -2 -4)^2
= (4)^2 + ( -2 -4)^2
= 16 + 36 = 52
BC^2 = ( 5 + 1)^2 + ( 2 + 2)^2
= 6^2 + 4^2
= 36 + 16
= 52
CA^2 = (-5 -5)^2 + (4 - 2)^2
= (-10) + 2^2
= 100 + 4
= 104
AB^2 = BC^2
AB = BC
△ABC is an isosceles triangle
AB^2 + BC^2 = 52 + 52 = 104 = CA^2
△ABC is a right triangle.
Hence △ABC is isosceles right triangle.
Q 9. The centre of a circle is ( 2, 6) and its radius is 13 units. Find x, if P( x, 2x) is a point on the circumference of the circle.
Solution
Centre of a circle is O(2,6) and its radius is 13 units.
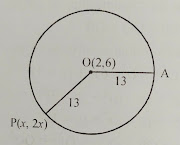 P(x, 2x) is a point on the circumference of the circle.
P(x, 2x) is a point on the circumference of the circle.
Join OP
OP^2 = (x2 - x1)^2 + (y2 - y1)^2
13^2 = (2 - x)^2 + (6 - 2x)^2
169 = 4 + x^2 - 4x + 36 + 4x^2 - 24x
169 = 5x^2 - 28x + 40
5x^2 - 28x +40 -169 = 0
5x^2 - 28x +40 -129 = 0
5x^2 + 15x - 43x -129 = 0
5x(x + 3) - 43(x + 3) = 0
(x + 3) (5x - 43) = 0
either (x + 3) = 0 or (5x - 43) = 0
=√ (1 + 2)^2 + ( 4 - 2 )^2
=√ 3^2 + 2^2
=√ 9 + 4
=√ 13
=√ (7 - 1)^2 + ( 8 - 4 )^2
=√ 6^2 + 4^2
=√ 36 + 16
=√ 52 = 2√13
=√ (-2 - 7)^2 + ( 2 - 8 )^2
=√ -9^2 + -6^2
=√ 81 + 36
=√ 117 = √9 * 13 = 3√13
PQ + QR = √13 + 2√13 = 3√13
Sum of two sides of equal to the third side
Thus P, Q and R lies on same straight line.
P,Q,R are collinear.



Post a Comment